Diseases That Affect the Tongue
How does the healthy tongue look?
The tongue should be a pinkish to reddish in color on the top of the tongue and should be pink with bluish hue on the underside as some veins may be seen. The tongue should have a rough top surface due to the taste buds and the underside of the tongue should be smooth. There should be no hairs, furrows, or ulcerations. The tongue should fit comfortably in the mouth with the tip against the teeth.
What can cause a tongue to look smooth and shiny?
If the tongue is not smooth because of rubbing against the teeth, crowns, implants or a denture than nutritional deficiency may be the culprit. Vitamin deficiency, especially vitamin B12 deficiency (pernicious anemia), can be the cause. Other deficiencies that can contribute include vitamin B3, B6, B9, and iron.
What causes the tongue to look white?
- Oral candidiasis (thrush), is an infection of a fungus called Candida albicans that can make the tooth look white and furry. Immunosuppression such as (HIV), diabetes, denture use without teeth cleaning, and/or antibiotic use (usually over long-term periods).
- Oral lichen planus is an autoimmune disease that has a white lace-like pattern called reticular lichen planus.
- Geographic tongue is a non-cancerous problem with painless patches on the tongue that can appear, disappear, and then reappear in a different area. This is seen in 1%–3% of the population. Recent evidence, however, suggests that geographic tongue may be linked with a Vitamin B3 deficiency and inflammation of the intestine or leaky gut.
- Vitamin Deficiency in Vitamin A, Vitamin B2, B3, B6, B9, and B12
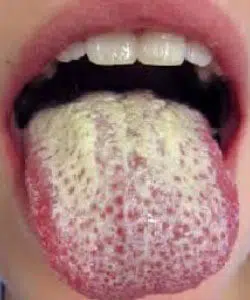
White tongue: Candida albicans fungal infection sometimes referred to as thrush
What causes the tongue to look red?
A red tongue can be a sign of a vitamin deficiency (B2, B6, B9, B12) Iron deficiency, protein deficiency such as Kawasaki disease, or a strep infection (scarlet fever). Red ulcerations of the tongue can be signs of cell changes and red ulcerations lasting more than 2 weeks should be biopsied.
What causes the tongue to look black?
A black tongue is usually a harmless condition that can be caused by chlorohexidine rinses (Peridex), medications, smoking, antibiotic use, poor oral hygiene, soft diet, or dry mouth. The cause of black tongue is thought to be a change in the normal bacteria in the mouth after antibiotic treatment or use of products that contain bismuth (sulfa), such as Pepto-Bismol.
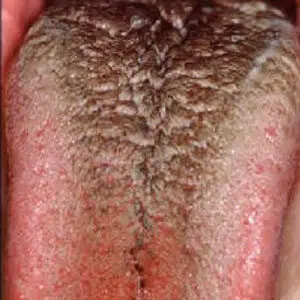
Black, hairy tongue from poor oral hygiene and smoking
What causes a change in taste?
- Medications usually cause a metallic taste, and these are associated with some forms of antibiotics; chlorhexidine rinses; antihistamines; antifungals; antipsychotics; blood pressure, diabetes, seizure, and Parkinson’s disease medications; among others.
- Covid-19 has been associated with changes in taste because due to the SARS CoV-2 virus affects the ACE-2 receptors in the tongue and nose.
- Dry Mouth caused by colds or flu, smoking, and nutritional deficiencies (Vitamin B12, Vitamin C, and Zinc).
What causes the tongue to have ulcers?
Tongue ulcers that do not heal or regress in 10–14 days should be of concern and either biopsied or referred to a specialist.
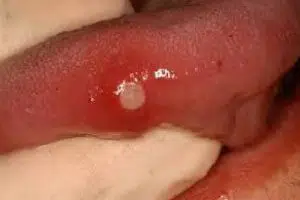
- Canker sores (aphthous ulcer)is a painful form of ulceration frequently encountered. The ulcer appears in one of several patterns: minor (small that heal within 14 days), major (large and may scar when they heal), or herpetiform (multiple pinpoints that can combined into 1 large ulcer).
- Recurrent canker sores occur in some systemic illnesses, including Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, Behcet’s syndrome, pemphigus, herpes simplex, histoplasmosis, and reactive arthritis (Reiter’s syndrome).
Minor canker sore white in appearance with a red border frequently found on the lateral border of the tongue
Call 212-751-8530 today to schedule a consultation with Dr. Froum or request an appointment.
